Refractive Surgery (Lasik)
About Lasik
LASIK stands for Laser-Assisted In-Situ Keratomileusis and is a procedure that permanently changes the shape of the cornea, the clear covering of the front of the eye, using an excimer laser. LASIK is a surgical procedure intended to reduce a person's dependency on glasses or contact lenses.
LASIK has advantages over other procedures, including a relative lack of pain afterward and the fact that good vision is usually achieved almost immediately, or at least by the very next day.


Refractive Surgery
An instrument called microkeratome is used in LASIK eye surgery to create a thin, circular flap in the cornea. The surgeon folds the flap back out of the way, then ablates a predetermined amount of corneal tissue underneath using an excimer laser.
The laser uses a cool ultraviolet light beam to precisely remove ("ablate") very tiny bits of tissue from the cornea to reshape it. When the cornea is reshaped in the right way, it works better to focus light into the eye and onto the retina, providing clearer vision than before.
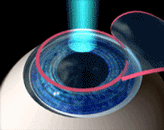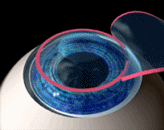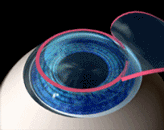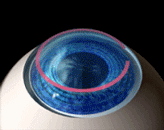
Both nearsighted and farsighted people can benefit from the LASIK procedure. With nearsighted people, the goal is to flatten the too-steep cornea; with farsighted people, a steeper cornea is desired. Also, excimer lasers can correct astigmatism, by smoothing an irregular cornea into a more normal shape.
In order to decide whether the patient is a good candidate for LASIK, our specialists will examine his/her eyes to determine their health, what kind of vision correction is needed, and how much laser ablation is required.
Accessory with MEL 80 is a corneal topographer which photographs the reflection of a target on eyes and creates a kind of "map" of your cornea. No one has a perfectly rounded cornea, and the topographer will display the corneal irregularities and the steepness or flatness that the surgeon must correct.